
The kanban is a key element of the "Just in Time" production system.
Kanban tries to simplify and visualise logistics, production and development by operating on the quantities of inventory and tasks in the phases - in many cases very effectively.
Some people see it as one of the best alternatives to Scrum, but we prefer to think that these tools can be complementary.
But what does it mean, what are its advantages and disadvantages, and is it worth replacing Scrum?
The Kanban system
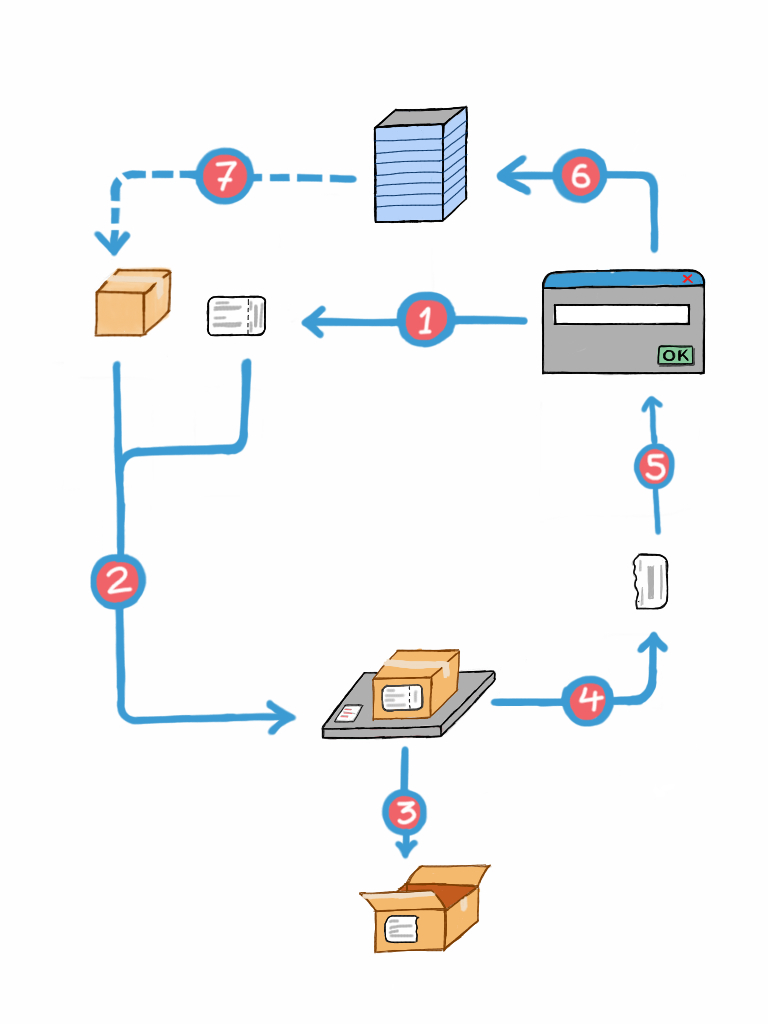
The history of kanban dates back to the mid-20th century.
Like many other production systems, it is thanks to Japan, the Toyota factory and Toyota legend Taiichi Ohno.
Kanban means card or board in Hungarian - but it actually expresses a sign that is made with cards or boards.
Unlike the classic push systems, the kanban is a pull method. This means that, unlike push, where a kind of pushing process takes place based on demand, in kanban the process is driven by the quantities given.
What does it mean?
The kanban method limits the amount of raw material or task in a given work phase. Different kanban elements can be used to indicate whether supplies are needed.
The tools and signs work differently everywhere, but the general basis of the kanban system is the kanban board along a visualised workflow.
Kanban can reduce stocks - and it does it very simply. In many cases, this is the source of the problem.
Advantages and disadvantages of Kanban
The system does not focus on the demand in the first place, but on the process through which the demand is fulfilled. At the kanban, production/development is controlled by specified quantity limits, which can significantly reduce overproduction and quickly and easily optimise the system along customised metrics (e.g. lead times, throughput times).
Kanban provides a visual representation of the workflow and significantly reduces the number of parallel tasks, which can reduce waste according to lean principles.
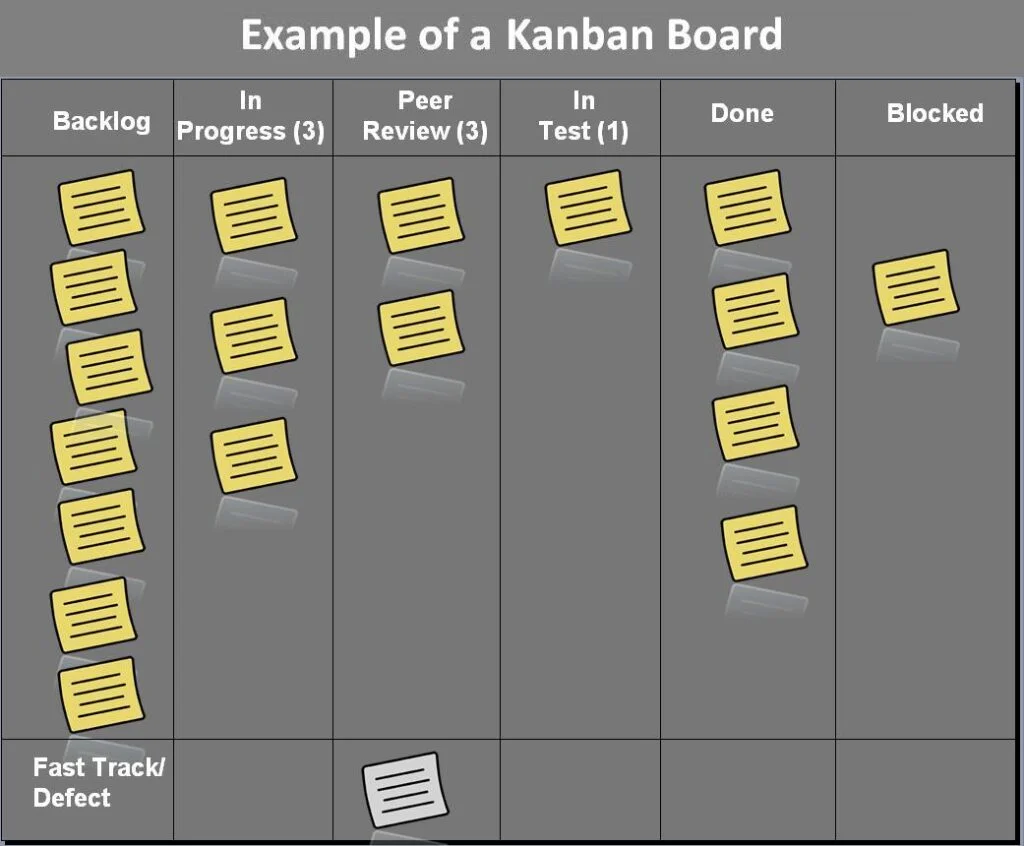
The strength of the system is that it is simple, but it requires a huge amount of self-discipline on the part of the organisation.
This can also be true for the Scrum methodology, so what is the main difference between Kanban and Scrum?
Kanban vs. Scrum
The difference between the two systems is that Scrum creates value in iterations, called sprints, while Kanban creates value in a continuous flow. While in Scrum, Sprint Planning or Sprint Overview are important foundational elements, Kanban considers them as unnecessary obstacles and provides a continuous flow instead of sprints.
Another important difference is that the introduction of Scrum usually requires a major reorganization, a change in the way of working, while kanban suggests that to increase efficiency, start with the current environment without major reorganization, "start from what is now".
But which system should you use?
The choice depends on the characteristics of the tasks and the environment. If the Scrum is already working well, the kanban board can also function as a supplementary tool as a kind of Scrumban system.
Typically, kanban is optimal for more "mature" products where there is an established, functioning value creation process.
Kanban can also be a good solution for those who want to find out where the problems are in the value creation process.
So the kanban system:
- It visualises the processes for everyone.
- It makes production and development easily traceable.
- It makes the process measurable and controllable.
Summary
Kanban is a great system, but it requires a great deal of self-discipline on the part of an organisation to be effective.
Kanban is a completely autonomous system that can be used in several areas (e.g. IT, HR, sales, manufacturing).

 Designabc
Designabc